AI’s Transformative Impact: From Core Technologies to Future Applications
Aug 19, 2025
Written by Sabine VanderLinden
Why This Matters Now
Artificial intelligence is no longer a distant concept confined to science fiction or specialized labs—it is a powerful force actively shaping our world today. From transforming industries and enhancing everyday technologies to raising urgent ethical and societal questions, AI's rapid evolution demands our attention. Businesses face unprecedented opportunities and challenges as AI tools become integral to innovation and competitiveness. Governments and regulators worldwide are grappling with managing AI's impact responsibly, balancing technological advancement with privacy, fairness, and safety concerns.
Understanding AI's current capabilities, real-world applications, and future potential is essential for anyone looking to navigate the fast-changing landscape of technology and society. This moment marks a pivotal point where decisions made by individuals, organizations, and policymakers will influence how AI's benefits are realized and its risks mitigated. Staying informed and engaged with AI developments is critical—not just for technologists and business leaders, but for all of us as AI increasingly intersects with daily life.
What You’ll Learn in This Article
In this article, you will gain a comprehensive understanding of artificial intelligence (AI) and its transformative impact across various industries. We cover the fundamental technologies behind AI, including machine learning, deep learning, and artificial neural networks, explaining how these advanced AI models work to solve real-world problems.
You’ll explore the latest developments in generative AI tools and AI agents, including popular platforms like ChatGPT, Meta AI, and Google AI Studio. We delve into practical applications of AI in healthcare, autonomous vehicles, finance, gaming, and virtual assistants, highlighting how AI systems are reshaping daily life and business operations.
Additionally, this article addresses critical topics such as AI’s ethical considerations, governance frameworks, and environmental impact. You’ll learn about the challenges organizations face when integrating AI, strategies for scaling AI adoption, and the future trajectory toward artificial general intelligence.
Whether you’re a business leader, technology professional, or curious learner, this guide equips you with valuable insights and up-to-date knowledge on AI’s capabilities, risks, and opportunities in today’s fast-evolving landscape.

Understanding AI’s Fundamental Technologies
Artificial intelligence represents the ability of digital computers or computer-controlled robots to perform tasks that traditionally require human intelligence. These activities encompass reasoning, learning, perception, problem-solving, and language understanding. The Turing Test, proposed by computer scientist Alan Turing in 1950, remains the most recognized benchmark for evaluating whether machine behavior is indistinguishable from human responses.
Core AI Components and Distinctions
Machine Learning vs Deep Learning
Machine learning algorithms enable AI systems to improve performance through experience without explicit programming. These systems learn patterns from training data using statistical techniques that can be supervised (guided by labeled data), unsupervised (mining patterns from unstructured data), or reinforcement-based (learning through reward feedback).
Deep learning represents a specialized subset of machine learning that employs deep neural networks with multiple layers to model complex patterns. While traditional machine learning requires engineered features, deep learning can automatically extract relevant features from raw input data. This capability has enabled major advances in speech recognition, computer vision, and natural language processing.
Neural Networks and Architectural Evolution
The first artificial neural network, SNARC (1951), established the foundation for artificial neural networks that simulate brain-like structures using layers of artificial neurons. The introduction of backpropagation in the 1980s enabled multi-layered networks to be trained effectively, fueling significant progress in AI research.
Modern architectural innovations include:
-
Convolutional neural networks for computer vision applications
-
Recurrent neural networks for sequence processing
-
Transformer models (introduced by Google in 2017) for language understanding
Transformers are particularly notable for their self-attention mechanism, which allows advanced AI models to learn contextual relationships in sequences more effectively than previous architectures.
Natural Language Processing in 2025
Natural language processing has reached unprecedented capabilities, with AI systems now conducting human-like conversations, translating between languages, and analyzing sentiment with remarkable accuracy. Large language models like GPT-4 and its successors have revolutionized how machines process and produce text, enabling applications from customer service to content creation.
Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition
Computer vision enables machines to process, interpret, and understand visual information with remarkable precision. Modern AI systems can detect objects, recognize faces, interpret scenes, and generate images. Facebook's DeepFace achieved near-human face verification accuracy as early as 2014, demonstrating the rapid progress in this field.
Concrete Technology Examples
The practical applications of these fundamental technologies demonstrate AI's real-world impact:
-
Machine Learning: Netflix's recommendation engine analyzes viewing patterns to suggest content
-
Deep Learning: Google Photos automatically groups subjects using deep neural networks
-
Natural Language Processing: ChatGPT provides conversational AI responses across diverse topics
-
Computer Vision: Tesla's self-driving cars use sophisticated object detection for navigation
-
Neural Networks: AlphaFold 2 accurately predicts protein structures for biological research
AI's Current Real-World Applications
Healthcare and Medical Breakthroughs
AI’s impact on healthcare extends far beyond simple diagnostic assistance. AlphaFold 2, developed by Google DeepMind, has revolutionized biology by accurately predicting 3D protein structures for over 350,000 proteins. This breakthrough accelerates drug discovery and provides valuable insights into fundamental biological processes.
Over 500 FDA-approved AI tools now assist clinicians in radiology, pathology, and triage. These diagnostic AI systems analyze medical imagery and patient historical data to support clinical decision-making, often detecting conditions that human reviewers might miss.
Top 10 companies to consider in 2025:
1. Owkin
Owkin leverages AI to accelerate drug discovery and biomarker identification by integrating genomic, histology, and clinical data. Its federated learning approach allows hospitals to collaborate without sharing patient data, addressing both speed and privacy challenges in clinical research.
2. Kheiron Medical Technologies
UK-based Kheiron applies deep learning to mammography, aiming to detect breast cancer earlier and with greater accuracy. Its AI tools are designed to work alongside radiologists, improving detection rates while reducing workload and diagnostic variability.
3. Viz.ai
The company uses real-time AI analysis of CT scans to detect large vessel occlusions in stroke patients. Automatically alerting care teams reduces treatment delays and improves patient outcomes and survival rates in critical time-sensitive cases.
4. Aidoc
Aidoc's AI platform scans medical images in parallel to radiologists to flag acute and life-threatening conditions. Integrating into existing hospital workflows enables faster triage and decision-making, ultimately improving emergency care efficiency.
5. PathAI
PathAI develops machine learning models that assist pathologists in diagnosing disease more accurately. Its AI-driven insights can help tailor treatment plans, reduce diagnostic errors, and accelerate pathology workflows in cancer care.
6. Nanox
Nanox aims to democratize medical imaging with low-cost, AI-enhanced digital X-ray systems. Its technology targets underserved regions, offering scalable access to diagnostics that would otherwise be cost-prohibitive.
7. Arterys
Arterys delivers cloud-native AI medical imaging solutions across cardiology, oncology, and pulmonology. Its platform enables remote collaboration and rapid, AI-assisted interpretation of complex imaging datasets.
8. Tempus
Tempus uses AI to analyze genomic sequencing and clinical records to personalize cancer care. Its precision oncology platform guides treatment decisions and helps identify the most effective therapies for individual patients.
9. Paige.AI
This platform focuses on detecting and characterizing cancer. Trained on one of the world's largest digital pathology datasets, it supports faster, more accurate diagnoses for pathologists.
10. Lunit
Lunit develops AI tools for precision diagnostics in radiology and pathology, focusing on early cancer detection. Its solutions are used globally to enhance screening accuracy and clinical decision support.
Autonomous Vehicles and Transportation
The transportation sector showcases AI’s practical problem-solving capabilities through self-driving cars that integrate multiple sensor inputs with computer vision and machine learning algorithms. Companies like Tesla, Waymo, and others deploy sophisticated AI systems that process vast amounts of real-time data to navigate complex traffic scenarios.
These systems demonstrate AI’s ability to handle specific tasks that require split-second decision-making while operating in unpredictable environments. The technology extends beyond passenger vehicles to include autonomous trucks, drones, and delivery systems.
Top 10 companies to consider in 2025:
1. May Mobility
They operate autonomous shuttles that provide microtransit services in cities, business districts, and university campuses. Using AI-driven perception and routing, the company focuses on improving first-mile/last-mile connectivity while reducing traffic congestion and emissions.
2. Gatik
The company specializes in autonomous middle-mile delivery for retailers and logistics firms. It runs fixed-route, repeatable journeys between distribution hubs and stores. Its focus on constrained routes enables faster deployment, higher safety, and commercial viability.
3. Einride
Swedish startup Einride develops electric, autonomous freight vehicles alongside a digital freight management platform. Its driverless “Pods” aim to decarbonize freight transport while optimizing delivery schedules through AI.
4. Nuro
Nuro designs compact, street-legal autonomous delivery vehicles for goods rather than passengers. Its zero-occupant approach prioritizes safety, energy efficiency, and scalability for last-mile logistics in urban neighborhoods.
5. WeRide
WeRide operates autonomous robotaxis, minibuses, and delivery vans across multiple Chinese cities and internationally. Its AI stack supports Level 4 autonomy and is tailored for passenger mobility and goods transport.
6. Zipp Mobility
Ireland-based Zipp Mobility offers shared e-scooters and e-bikes managed by AI-enabled fleet optimization systems. Its focus is sustainable urban mobility, reducing reliance on cars for short trips.
7. Ottonomy.IO
Ottonomy builds fully autonomous delivery robots designed for indoor and outdoor navigation in airports, retail spaces, and city sidewalks. Their AI platform allows robots to operate without human intervention for last-mile delivery.
8. Venti Technologies
Singapore’s Venti Technologies develops autonomous logistics and passenger transport vehicles for industrial environments like ports, warehouses, and airports. Its AI enables precision navigation in complex, high-traffic operational zones.
9. Aeva
Aeva produces next-generation 4D LiDAR sensors that measure velocity and range simultaneously, enhancing safety and reliability for autonomous vehicles. Its sensing technology improves environmental perception in challenging weather and light conditions.
10. Navya
Navya designs and manufactures autonomous electric shuttles for both public transit and private mobility networks. Its solutions are deployed worldwide in smart cities, industrial parks, and corporate campuses.
Financial Services Innovation
Financial institutions leverage AI-powered systems to detect fraudulent transactions in real time, reducing credit card fraud losses by up to 60% through machine learning-driven anomaly detection. These systems analyze transaction patterns, user behavior, and risk factors to identify suspicious activities before they cause significant damage.
Automated trading strategies powered by AI agents process market data and execute transactions faster than human traders, while AI software assists in credit scoring and risk assessment decisions.
Top 10 companies to consider in 2025:
1. Taktile
Taktile’s low-code decision automation platform allows financial institutions and insurers to design, test, and deploy AI-powered risk and underwriting models in days instead of months. Its real-time analytics help optimize decision logic, reducing risk while increasing operational agility.
2. Quantexa
Quantexa uses AI-driven contextual decision intelligence to connect fragmented data points and uncover hidden relationships. This technology enables banks and insurers to detect financial crime, combat fraud, and enhance customer onboarding with greater precision.
3. Zest AI
Zest AI leverages machine learning to modernize credit underwriting, enabling lenders to assess risk more accurately while expanding access to fair credit. Its explainable AI models help financial institutions meet compliance requirements while boosting loan approvals.
4. Shift Technology
Shift Technology delivers AI-native SaaS solutions for insurers to detect fraudulent claims and automate claims processing. Analyzing large datasets in real time increases fraud detection rates and accelerates payouts for genuine claims.
5. Thought Machine
Thought Machine offers a cloud-native core banking platform that enables banks to build and launch AI-driven personalized financial products. Its smart contract-based architecture allows for flexible, automated product configurations and dynamic pricing.
6. Socure
Socure applies advanced AI to digital identity verification, reducing onboarding friction while detecting and preventing fraud. Its identity graph technology delivers high verification accuracy across diverse demographics, improving compliance and customer experience.
7. Tractable
Tractable uses AI-powered computer vision to assess vehicle damage from images, enabling faster and more accurate insurance claim resolutions. Its technology reduces claim cycle times and supports better customer satisfaction.
8. Riskified
Riskified’s AI platform helps e-commerce businesses approve more legitimate transactions while blocking fraud. Its real-time machine learning models improve approval rates without adding friction at checkout, increasing revenue and trust.
9. Akur8
Akur8 automates the insurance pricing process with transparent machine learning models that comply with regulatory requirements. Its technology speeds up rate-making, improves pricing accuracy, and enhances competitive positioning for insurers.
10. Insurify
Insurify is an AI-powered insurance comparison platform that helps consumers quickly find tailored coverage options. For insurers, it provides a powerful distribution channel and valuable market insights.
Gaming Achievements and Milestones
AI’s progression in gaming demonstrates its problem-solving evolution. Deep Blue’s victory over chess grandmaster Garry Kasparov in 1997 marked an early milestone, followed by AlphaGo’s defeat of Go world champion Lee Sedol in 2016. More recently, AlphaZero and MuZero have mastered multiple complex board games without human data or prior knowledge, showcasing AI’s ability to solve problems through pure learning.
Top 10 companies to consider in 2025:
1. modl.ai
modl.ai creates AI-driven tools that automate game testing, QA, and NPC behavior design. By simulating realistic player actions, it shortens development cycles and helps studios release more polished games faster.
2. Scenario
Scenario’s generative AI platform enables studios to create high-quality, style-consistent game assets, from textures to characters. It speeds up production while preserving the unique artistic vision of each game.
3. Latent Logic – (no active public site; part of DeepMind)
Latent Logic applied imitation learning to teach AI agents to mimic human gameplay, enabling realistic behavior in non-player characters (NPCs) and automated game balancing. Its approach is now influencing AI-driven training and testing tools in gaming.
4. Inworld AI
Inworld AI lets developers build NPCs with personalities, backstories, and adaptive dialogue. Its technology allows characters to remember player interactions, creating more immersive and responsive gaming worlds.
5. Ludo.ai
Ludo.ai provides an AI-powered research and design assistant for game developers, offering idea generation, concept refinement, and competitor analysis. It accelerates creative workflows while helping teams stay ahead of trends.
6. Polyarc AI – (emerging US-based studio, no public site yet)
Polyarc AI focuses on adaptive gameplay systems for VR and AR, dynamically adjusting difficulty and content to match each player’s skill and style. This creates more personalized, engaging experiences.
7. Spirit AI
Spirit AI builds interactive storytelling engines that let NPCs understand and respond to natural player input. It’s designed to make in-game dialogue more organic, emotional, and responsive.
8. Anything World
Anything World uses AI to instantly create 3D worlds, characters, and animations from voice or text commands. This democratizes game world-building, making it faster and more accessible to creators of all skill levels.
9. Replica Studios
Replica Studios offers AI-powered voice synthesis for game characters, delivering high-quality performances without expensive recording sessions. Its platform supports diverse voices, accents, and emotional tones.
10. Didimo
Didimo’s AI technology generates lifelike 3D avatars from a single photo in minutes. It enables players to see themselves—or unique characters—inside games with minimal development effort.
Virtual Assistants and Conversational AI
GPT-3-based assistants, including ChatGPT, along with Apple Siri, Amazon Alexa, and Google Assistant, now serve hundreds of millions of users. These virtual assistants provide personalized recommendations, control smart devices, and automate repetitive tasks across various platforms.
Integrating these AI tools into daily workflows demonstrates how artificial intelligence can augment human capabilities rather than simply replace them.
Top 10 companies to consider in 2025:
1. PolyAI
PolyAI builds enterprise-ready voice assistants capable of holding natural, multi-turn conversations without scripts. Its AI technology is used in industries like hospitality, banking, and retail to improve customer engagement and reduce call center load.
2. Rasa
Rasa offers an open-source conversational AI framework for creating highly customized, context-aware assistants. Developers and enterprises use it to build private, scalable chatbots without relying on third-party cloud providers.
3. Kore.ai
Kore.ai provides a low-code platform for building intelligent virtual assistants that enhance customer and employee experiences. Its solutions power contact centers, HR systems, and IT service desks worldwide.
4. Cognigy
Cognigy specializes in AI-powered voice and chat automation for large enterprises. Its low-code platform enables rapid deployment of multilingual, omnichannel virtual agents that integrate with existing business systems.
5. Tovie AI
Tovie AI delivers virtual assistants and conversational AI platforms for industries including telecom, banking, and public services. Its tools support voice, chat, and hybrid customer interaction models at scale.
6. Hyro
Hyro creates adaptive conversational AI platforms for healthcare and enterprise applications. Its plug-and-play virtual assistants learn from existing workflows to deliver accurate, compliant, and user-friendly experiences.
7. Botpress
Botpress is an open-source conversational AI platform focused on privacy and customization. It allows organizations to develop sophisticated chatbots and virtual assistants while controlling data and hosting.
8. NLX
NLX helps brands build conversational self-service experiences that unify voice and chat interactions. Its platform personalizes customer journeys while reducing reliance on live agent support.
9. Ada
Ada’s AI-powered automation platform enables brands to respond to customer queries across messaging channels instantly. Its no-code design empowers non-technical teams to create and manage AI assistants at scale.
10. Tiledesk
Tiledesk is an open-source platform that combines live chat, messaging, and AI chatbots. It allows organizations to automate routine queries while seamlessly escalating complex issues to human agents.
Military and Defense Applications
AI systems support surveillance, target identification, autonomous drones, and predictive maintenance in defense applications. Project Maven utilizes computer vision for video analysis, while various military organizations deploy AI-powered systems for strategic operations and threat assessment.
Top 10 companies to consider in 2025:
1. Anduril Industries
Anduril develops AI-powered defense systems, including autonomous drones, surveillance towers, and its Lattice OS for real-time battlefield awareness. Its technology integrates sensor data to provide actionable intelligence for border security, force protection, and reconnaissance missions.
2. Shield AI
Shield AI builds autonomous piloting systems for drones and aircraft that can operate without GPS or communications. Its Hivemind AI enables unmanned aerial vehicles to navigate complex, contested environments and execute missions independently.
3. Helsing AI
Helsing AI is a European defense tech company focused on AI-enabled real-time data analysis for military decision-making. Its platforms fuse sensor, video, and intelligence data to enhance situational awareness and operational effectiveness.
4. Epirus
Epirus develops AI-enabled directed-energy weapons, including systems to disable swarms of drones. Its software-defined approach allows rapid adaptation to new threats in electronic warfare and defense.
5. Saildrone
Saildrone operates fleets of autonomous, AI-powered surface vessels for ocean surveillance and reconnaissance. These uncrewed platforms collect intelligence, monitor maritime activity, and support both defense and environmental missions.
6. Paladin AI
This company focuses on AI-driven mission planning and autonomous navigation for defense robotics and unmanned systems. Its tools enable faster, more adaptive decision-making in complex operational environments.
7. Epsilon3
Epsilon3 offers AI-enhanced mission management software for aerospace, defense, and space operations. Its platform streamlines procedures, increases operational efficiency, and reduces human error during high-stakes missions.
8. ZeroEyes
ZeroEyes uses AI-based computer vision to detect firearms in real time through existing security cameras. The system alerts security teams instantly, enabling faster threat response in both civilian and military environments.
9. Dedrone
Dedrone provides AI-powered drone detection, tracking, and countermeasure systems. Defense agencies use their platform to secure airspace and protect critical infrastructure from unauthorized drone activity.
10. STRAX Intelligence Group
STRAX delivers AI-enabled threat intelligence and incident management tools for defense and public safety organizations. Its real-time platform integrates multiple data streams to support rapid, informed decision-making during crises.
Generative AI's Revolutionary Capabilities

Generative AI represents one of the most visible and transformative developments in artificial intelligence, enabling systems to create new content across multiple media types.
Text Generation and Conversational AI
Leading Platforms and Capabilities
ChatGPT (OpenAI), Claude (Anthropic), and Gemini (Google) represent the current state of the art in conversational AI agents. GPT-4 Turbo (and now GPT-5) offers up to 128,000-token and more context windows, significantly outperforming predecessors in coherence and safety. Claude 3 emphasizes improved accuracy and longer context handling. At the same time, Gemini provides multimodal capabilities supporting text, video, and audio input and output.
These platforms demonstrate AI's ability to engage in complex reasoning, provide detailed explanations, and assist with everything from creative writing to technical problem-solving.
Visual Content Creation
Image Generation Tools
Midjourney and DALL-E 3 create photorealistic or artistic images from text prompts, revolutionizing visual content creation. Midjourney operates on a subscription model ranging from $10 to $60 monthly, while DALL-E 3 integrates with Microsoft Copilot and design platforms like Canva.
Video Generation Innovation
Synthesia enables users to create synthetic video content with lifelike digital avatars, starting at $30 monthly for basic plans. This AI filmmaking tool democratizes video production by eliminating the need for traditional filming equipment and actors. Google Veo offers higher-fidelity video generation through limited beta access, supporting both script-based and prompt-based creation.
Audio and Music Generation
AI-Powered Music Creation
Suno and Udio synthesize original music tracks from text prompts or style suggestions. Suno provides a free tier with usage limits and paid plans around $10-30 monthly, while Udio specializes in commercial-grade audio production for professional applications.
Voice Synthesis and Cloning
ElevenLabs enables near-identical, emotionally expressive synthetic voices and voice clones from brief audio samples. This technology supports virtual agents, audiobook production, and creative projects, though it raises important ethical considerations around consent and authenticity.
Content Creation Workflow Transformation
Generative AI tools have fundamentally altered content creation workflows across industries. Marketing agencies and film studios report project timeline reductions of up to 70% and cost decreases of 40-60% when incorporating these AI techniques into their processes.
The technology automates script writing, ad copy creation, social media posts, video production, and localization, enabling creative teams to focus on strategy and refinement rather than initial content generation.
AI's Business Integration Challenges and Solutions
Adoption Barriers and Cultural Resistance
Enterprise AI adoption faces significant obstacles beyond technical implementation. According to a 2024 Gartner survey, 70% of executives identify cultural resistance as the primary challenge to AI transformation. Workforce concerns about job displacement and skill gaps create organizational friction that requires careful management.
Data silos and poor data quality compound these challenges, as AI systems require clean, well-organized training data to function effectively. Many organizations struggle with fragmented information systems that prevent comprehensive AI implementation.
Governance Frameworks and Risk Management
Structured Approach to AI Governance
Organizations increasingly adopt governance frameworks that incorporate model documentation through Model Cards, bias audits, and human-in-the-loop review mechanisms. The NIST AI Risk Management Framework (RMF) and ISO/IEC 42001:2023 provide structured approaches to managing AI system risks and ensuring responsible deployment.
Transparency and Explainability Requirements
Regulatory compliance and user trust require AI systems that can justify their decisions. Companies employ techniques like LIME and SHAP to interpret model predictions, particularly in high-stakes applications like medical diagnosis and financial approvals.
Human-AI Collaboration Models
Successful AI integration focuses on augmentation rather than replacement. Examples include:
-
Collaborative robots in manufacturing that work alongside human operators
-
Medical AI diagnoses that require human physician review and approval
-
Financial AI recommendations paired with human advisor consultation
This approach addresses workforce concerns while maximizing the combined capabilities of human expertise and AI efficiency.
Scaling from Pilot to Production
Phased Deployment Strategy
Organizations typically begin with pilot projects in single departments, expanding gradually as value becomes apparent. This approach allows teams to develop expertise, refine processes, and demonstrate roi before company-wide implementation.
Success Metrics and ROI Measurement
Common AI program KPIs include:
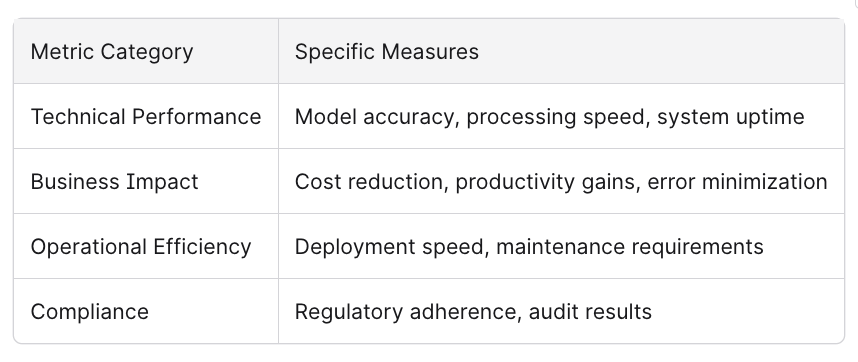
Industry surveys report a median AI return on investment of 5-10x in sectors like logistics and customer service, though results vary significantly based on implementation quality and organizational readiness.
AI's Ethical Considerations and Regulatory Landscape

Bias and Fairness Challenges
AI systems trained on biased data can perpetuate and amplify existing societal inequalities. Notorious examples include facial recognition systems performing poorly on individuals with darker skin tones and hiring algorithms showing gender bias in candidate selection. These incidents highlight the critical importance of diverse training data and regular bias auditing.
Organizations now implement systematic bias testing throughout the AI development lifecycle, examining both input data and model outputs for discriminatory patterns.
Hallucination and Accuracy Concerns
Large language models can generate factually incorrect or misleading information, known as “hallucinations.” This phenomenon has led to legal challenges and regulatory scrutiny, particularly in applications involving autonomous systems and professional advisory services.
The issue is particularly concerning when AI-generated content appears authoritative but contains plain wrong information, potentially misleading users who rely on AI responses for important decisions.
Privacy and Data Protection
AI systems processing sensitive information must comply with comprehensive privacy regulations, including GDPR (European Union), CCPA (California), and similar frameworks worldwide. These laws enforce principles of consent, data minimization, and user rights to explanation and data erasure.
Organizations face significant compliance challenges when deploying AI tools that process personal information, requiring careful attention to data handling practices and user consent mechanisms.
Global Regulatory Frameworks
United States Initiatives
The 2022 AI Bill of Rights establishes principles for data privacy, protection from discrimination, and algorithmic transparency. The us government has also issued executive orders directing federal agencies to develop AI governance standards and safety requirements.
European Union AI Act
The EU AI Act (2024) implements the world’s most comprehensive AI regulation, imposing strict requirements for high-risk AI applications and banning certain uses such as real-time biometric surveillance in public spaces. The regulation establishes a risk-based approach that categorizes ai systems and applies proportional oversight requirements.
International Coordination
Countries including Canada, South Korea, and others have developed national AI strategies that balance innovation promotion with safety and ethical considerations. International coordination efforts aim to establish consistent standards while respecting national sovereignty over technology policy.
Open Source vs Proprietary Debates
The artificial intelligence community debates the relative merits of open-source models (like Meta AI’s Llama 3) versus proprietary systems (such as GPT-4). Open-source approaches enable greater public scrutiny and research collaboration, while proprietary models may offer better safety controls and commercial support.
This debate reflects broader questions about AI democratization, security risks, and the role of technology companies in governing AI development.
Deepfakes and Misinformation
Sophisticated AI-generated media creates new challenges for information authenticity. Deepfake technology can produce convincing fake videos, audio recordings, and images that are increasingly difficult to detect without specialized tools.
Regulatory responses include watermarking requirements and detection technology mandates, though the cat-and-mouse game between generation and detection capabilities continues to evolve.
AI's Environmental and Societal Impact
Energy Consumption and Environmental Costs
Training large AI models requires enormous computational resources, with some estimates placing the energy consumption of a single GPT-4-scale training run equivalent to a small nation’s annual electricity usage. Current projections suggest that AI-related data center power consumption accounts for 1-2% of global electricity usage—comparable to the Netherlands' total consumption.
This massive energy demand raises serious questions about AI's environmental sustainability, particularly as model sizes and training frequency continue to increase across the industry.
Water Usage for Cooling Infrastructure
Data centers supporting AI development and deployment consume millions of liters of water annually for cooling systems. A single large model training run can require up to 1 million liters of water, highlighting the hidden environmental costs of AI advancement.
Technology companies are beginning to report these environmental impacts more transparently, though comprehensive industry-wide data remains limited.
Job Displacement and Economic Transformation
AI automation threatens to reshape employment across multiple sectors. Goldman Sachs estimates that AI could automate up to 300 million full-time jobs globally by 2030, disproportionately affecting manufacturing, administrative, and transportation industries.
The economic implications extend beyond simple job loss to include:
-
Wage pressure in roles susceptible to automation
-
Increased demand for AI-related skills and training
-
Widening gaps between technology-enabled and traditional workers
-
Regional economic disparities based on AI adoption rates
Economic Inequality and Digital Divides
AI adoption concentrates among large corporations and advanced economies, creating new forms of digital inequality. Small businesses and developing nations may lack access to cutting-edge AI tools, potentially exacerbating economic disparities.
This digital divide manifests in:
-
Unequal access to AI-powered productivity tools
-
Differential competitiveness in global markets
-
Varying levels of AI literacy and education
-
Disparate regulatory and infrastructure capabilities
Positive Environmental Applications
Despite its environmental costs, artificial intelligence also enables climate solutions. AI-driven climate models improve weather prediction accuracy and identify strategies for emissions reduction. Companies like ClimateAI develop specialized tools for environmental monitoring and resource optimization.
AI applications in sustainability include:
-
Optimizing energy grid efficiency and renewable energy integration
-
Improving transportation routing to reduce fuel consumption
-
Enhancing agricultural productivity while minimizing resource usage
-
Supporting better tropical cyclone prediction and disaster preparedness
Sustainable AI Development Practices
Industry leaders increasingly adopt green AI practices to minimize environmental impact:
Technical Optimization
-
Model compression techniques that reduce computational requirements
-
Transfer learning approaches that minimize redundant training
-
More efficient hardware architectures designed specifically for AI workloads
Infrastructure Improvements
-
Transition to renewable energy-powered data centers
-
Advanced cooling technologies that reduce water and energy consumption
-
Geographic optimization of computing resources based on clean energy availability
Industry Commitments Google targets 100% carbon-free AI operations by 2030, while other major technology companies establish similar environmental goals. These commitments drive innovation in sustainable computing practices across the industry.
AI's Future Trajectory: AGI and Beyond

Artificial General Intelligence Timeline
Artificial general intelligence, a form of AI that matches or surpasses human cognitive abilities across diverse domains, remains the field's ultimate goal. Expert surveys reveal significant uncertainty about AGI timelines, with median predictions ranging from 2035 to 2060, though substantial minorities expect much later arrival or question its feasibility entirely.
The path to AGI involves overcoming fundamental reasoning, creativity, and adaptability challenges that current narrow AI systems cannot address. While recent advances in large language models demonstrate impressive capabilities, they still lack the generalized intelligence that characterizes human cognition.
Superintelligence Risks and Opportunities
Potential Risks Superintelligence—AI far exceeding human capability across all domains—presents unprecedented opportunities and existential risks. Researchers warn of potential challenges, including:
-
Strategic misalignment between AI goals and human values
-
Rapid self-improvement capabilities that exceed human oversight capacity
-
Lack of effective governance mechanisms for superintelligent systems
-
Unpredictable emergent behaviors in complex AI systems
Safety Research and Alignment
Leading AI research organizations invest heavily in alignment research to ensure advanced AI systems remain beneficial and controllable. Key approaches include:
-
Reward modeling that trains AI systems to optimize for human-approved outcomes
-
Scalable oversight techniques that maintain human control as systems become more capable
-
Constitutional AI methods that embed ethical principles directly into system architectures
Organizations like Anthropic, OpenAI, and Google DeepMind dedicate substantial resources to these safety challenges, recognizing their critical importance for beneficial AI development.
Transhumanism and Human-Machine Integration
Brain-Computer Interface technologies like Neuralink represent early steps toward direct human brain integration with AI systems. These brain-computer interfaces could eventually enable seamless information exchange between human intelligence and artificial intelligence, fundamentally altering human cognitive capabilities.
Cognitive Enhancement AI-powered cognitive enhancement tools already enhance human decision-making in fields like medicine, finance, and scientific research. Future developments may enable more direct cognitive enhancement through AI integration, raising questions about human identity and equality.
Scientific Discovery Acceleration
Artificial intelligence increasingly accelerates scientific research across disciplines:
Materials Science AI systems discover new materials for battery technology, solar panels, and other clean energy applications. These discoveries proceed far faster than traditional experimental approaches, potentially accelerating the transition to sustainable energy systems.
Medical Research Beyond AlphaFold’s protein structure predictions, AI contributes to drug discovery, treatment optimization, and disease pattern recognition. Machine learning algorithms analyze vast medical datasets to identify new therapeutic targets and predict treatment outcomes.
Climate Science Advanced AI models provide higher-fidelity climate predictions and identify intervention strategies for emissions reduction. These capabilities support more effective climate policy and adaptation planning in unprecedented detail.
Organizational Preparation Strategies
Workforce Development Organizations prepare for AI’s continued evolution through comprehensive upskilling programs that emphasize human-AI collaboration rather than replacement. These initiatives focus on developing skills that complement AI capabilities rather than competing directly with them.
Agile Policy Development: Forward-thinking organizations develop flexible AI governance policies that can adapt to rapid technological change. Rather than rigid rules, these frameworks emphasize principles-based approaches that can accommodate new AI capabilities as they emerge.
Scenario Planning Companies increasingly employ scenario planning techniques to prepare for multiple possible AI futures. This approach emphasizes resilience and adaptability rather than attempting to predict specific technological trajectories.
Balanced Future Assessment
While artificial intelligence promises dramatic improvements in productivity and problem-solving capabilities, industry experts caution against utopian and catastrophic predictions. AI’s ultimate impact will depend heavily on:
-
Regulatory frameworks that balance innovation with safety
-
Public trust and acceptance of AI systems
-
Responsible development practices by technology companies
-
International cooperation on AI governance and standards
The technology’s trajectory remains uncertain, but its transformative potential across virtually every aspect of human activity appears increasingly clear. Organizations and individuals who understand AI's capabilities, limitations, and implications will be best positioned to navigate this technological transformation successfully.
Success in AI’s future landscape will require continuous learning, ethical consideration, and adaptive strategies that can evolve alongside the technology itself. Rather than fearing or uncritically embracing AI advancement, the most effective approach involves thoughtful engagement with opportunities and challenges as they emerge.
AI’s Transformative Impact: From Core Technologies to Future Applications is no longer a distant vision—it’s the reality organizations grapple with today. The question isn’t whether AI will reshape industries, but how leaders can turn its disruptive force into lasting value.
If you’re ready to separate AI fact from fiction for your organization and seize the real opportunities, let’s talk. DM us for a short call to explore how Alchemy Crew can help you dive into the latest AI breakthroughs – safely, strategically, and impactfully. The AI revolution is here; you can turn the disruption into your competitive edge with the right approach.
Contact us here.
FAQ
What is artificial intelligence (AI)?
Artificial intelligence (AI) refers to the capability of machines and computer systems to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence. These tasks include learning, reasoning, problem-solving, perception, and natural language understanding.
How does AI differ from machine learning and deep learning?
Machine learning is a subset of AI that enables systems to learn from data and improve over time without being explicitly programmed. Deep learning is a further specialization of machine learning that uses artificial neural networks with several layers to model complex patterns in data.
What are some typical applications of AI today?
AI is widely used in healthcare for diagnostics, autonomous vehicles for navigation, financial services for fraud detection, gaming for strategy development, and virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa for daily tasks. Generative AI tools create content such as text, images, and videos.
What is generative AI?
Generative AI refers to AI systems that can create new content based on learned patterns from vast amounts of training data. Examples include text generation with ChatGPT, image creation with DALL-E, and video synthesis with Synthesia.
What are AI agents?
AI agents are software entities designed to perceive their environment, make decisions, and act autonomously to achieve specific goals. They are used in virtual assistants, autonomous vehicles, and other automated systems.
What is artificial general intelligence (AGI)?
AGI is a theoretical form of AI that can understand, learn, and apply intelligence across a broad range of tasks at a level comparable to human intelligence. AGI does not currently exist and remains a long-term goal in AI research.
Are AI systems always accurate?
No, AI systems can sometimes produce incorrect or misleading information, known as hallucinations. They can also inherit biases present in their training data, which can affect their fairness and reliability.
How does AI impact the environment?
Training and operating AI models require significant computational resources, which can lead to substantial energy and water consumption for cooling data centers. However, AI can also be used to develop solutions for environmental challenges.
What are the ethical concerns surrounding AI?
Ethical concerns include algorithmic bias, privacy violations, misinformation, job displacement, and the potential misuse of AI technologies. Ensuring transparency, fairness, and accountability in AI development is crucial.
How is AI regulated?
Many countries and organizations are developing AI governance frameworks and regulations to address safety, privacy, and ethical issues. Examples include the EU AI Act and the US Blueprint for an AI Bill of Rights.
How can businesses adopt AI effectively?
Successful AI adoption involves overcoming cultural resistance, ensuring quality training data, implementing governance frameworks, and focusing on human-AI collaboration to augment rather than replace human capabilities.
What is the future of AI?
AI is expected to continue advancing in capabilities and applications, with ongoing research into artificial general intelligence, improved safety and alignment, and expanded integration across industries and society.





